
A Power over Ethernet (PoE) switch simplifies your network setup by delivering both data and power through a single Ethernet cable. This innovation eliminates the need for separate power sources for devices like IP cameras, VoIP phones, and wireless access points. With advancements in PoE technology, a single port can now supply up to 90 watts of power, supporting high-power devices. The global demand for PoE solutions continues to grow, with the market expected to reach $1.4 billion by 2026. A power over ethernet network switch not only streamlines installations but also supports the increasing need for connected devices in modern networks.
PoE switches make networks easier by sending power and data together. This uses one Ethernet cable and makes setup simpler.
PoE saves money by needing fewer cables. It also saves energy by turning off devices when not needed.
PoE switches let you place devices where there are no outlets. This is great for things like IP cameras and Wi-Fi points.
PoE switches can grow with your network. You can add devices easily without changing everything. This is helpful for expanding networks.
When picking a PoE switch, check how much power your devices need. Plan for future growth to keep your network working well.

Power over Ethernet (PoE) technology allows you to deliver both power and data to devices using a single Ethernet cable. This eliminates the need for separate power cables, simplifying installations and reducing clutter. For example, a digital security camera typically requires two cables—one for power and one for data. With PoE, you can connect the camera using just one cable, making it easier to deploy devices in hard-to-reach areas.
PoE technology supports a wide range of devices, including IP cameras, VoIP phones, LED lighting systems, and wireless access points. It also enables flexible network designs, allowing you to place devices where traditional power outlets may not be available. The IEEE 802.3bt standard further enhances PoE capabilities, delivering up to 100 watts of power to support high-performance devices like PTZ cameras and digital signage.
A power over ethernet network switch integrates data and electrical power into a single Ethernet cable. This process works by sending power over unused wire pairs in the cable or by combining power with data signals on the same pairs. The switch acts as the Power Sourcing Equipment (PSE), while the connected device, such as an IP camera or VoIP phone, is the Powered Device (PD).
For instance, when you connect a PoE-enabled device to the switch, the switch detects the device's power requirements and supplies the appropriate amount of power. This ensures safe and efficient power delivery without overloading the device. By using PoE, you can streamline the deployment of devices in challenging locations, such as ceilings or outdoor areas, without needing additional power outlets.
Benefits of this mechanism include:
Simplified installation for devices like wireless access points and IP cameras.
Reduced cabling requirements, which lowers costs and minimizes clutter.
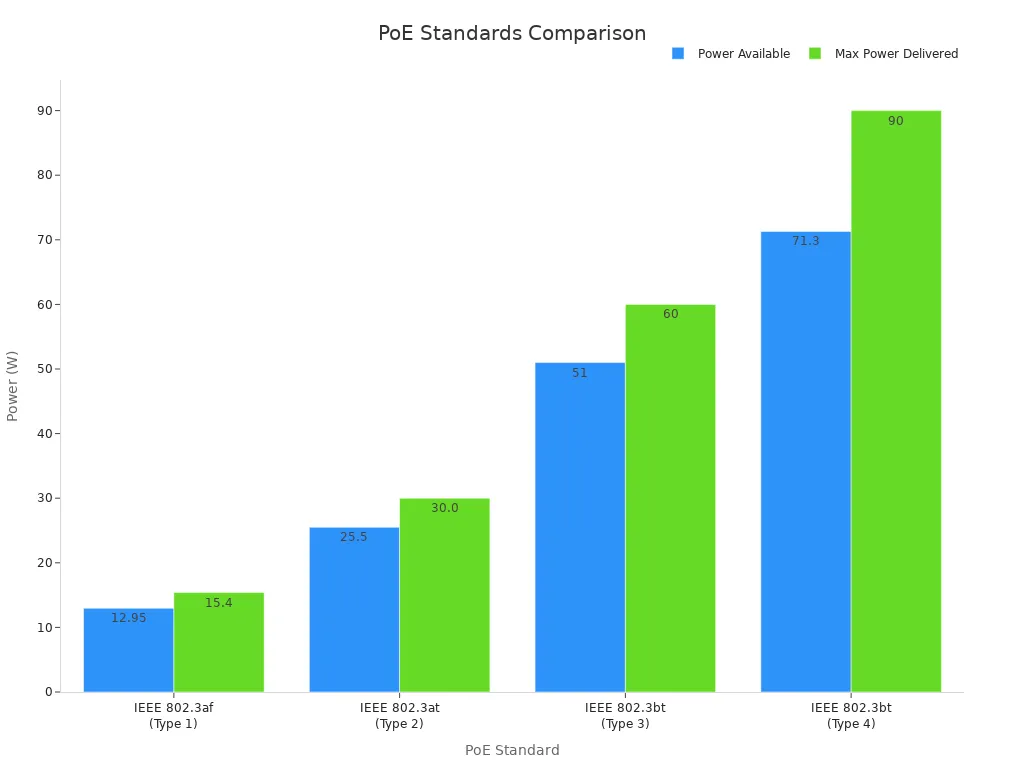
PoE standards define the amount of power that can be delivered to connected devices. These standards ensure compatibility and efficient power distribution across various devices. The most common PoE standards include:
PoE Standard | Power Available at PD | Maximum Power Delivered by PSE | Voltage Range (at PSE) | Maximum Current Imax | Power Management |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
IEEE 802.3af (Type 1) | 12.95 W | 15.40 W | 44.0–57.0 V | 350 mA | Three power classes (1–3) negotiated by signature |
IEEE 802.3at (Type 2) | 25.50 W | 30.0 W | 50.0–57.0 V | 600 mA per pair | Four power classes (1–4) negotiated by signature or LLDP |
IEEE 802.3bt (Type 3) | 51 W | 60 W | 52.0–57.0 V | 960 mA per pair | Six power classes (1–6) negotiated by signature or LLDP |
IEEE 802.3bt (Type 4) | 71.3 W | 90 W | 52.0–57.0 V | 960 mA per pair | Eight power classes (1–8) negotiated by signature or LLDP |
The IEEE 802.3bt standard, also known as PoE++, supports higher power levels, making it ideal for devices that require more energy. Each standard includes power classifications to ensure efficient power management, allowing you to connect multiple devices to a single power over ethernet network switch.
A Power over Ethernet network switch simplifies your setup by combining power and data delivery into a single Ethernet cable. This eliminates the need for separate power supplies and reduces the number of cables required. For example, instead of running both a power cable and a data cable to an IP camera, you only need one Ethernet cable. This streamlined approach minimizes installation complexity and saves time.
Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
Simplified Installation | PoE technology allows Ethernet cables to carry both power and data, reducing the need for extra power supplies and cabling. |
Reduced Cabling | By using PoE, the number of cables required is minimized, leading to lower installation complexity and costs. |
This simplicity makes PoE switches ideal for deploying devices in hard-to-reach areas, such as ceilings or outdoor locations, where running multiple cables would be challenging.
Switching to PoE technology can significantly reduce your operational costs. A case study of a medium-sized business with 100 IP cameras and 50 wireless access points showed that using managed PoE switches and implementing power scheduling reduced energy consumption by 35%. This saved the company over $3,000 annually on electricity bills.
PoE technology also helps conserve energy by allowing devices to automatically turn off when not in use. For example, lights connected to a PoE system can shut down during non-working hours, further lowering energy costs. By centralizing power management, you can reduce expenses while maintaining an efficient network.
PoE switches give you the freedom to install devices in locations without power outlets. This flexibility is especially useful for security cameras, which can be placed in remote or outdoor areas. Wireless access points can also be positioned for optimal coverage, improving connectivity across your space.
Key advantages of flexible placement include:
Installing devices in areas without power outlets.
Positioning wireless access points for better signal strength.
Deploying digital signage and IoT devices without power constraints.
Relocating devices easily without additional wiring.
This adaptability makes PoE switches a practical choice for expanding networks and accommodating future needs.
A power over ethernet network switch offers an excellent solution for growing networks. As your needs evolve, you can easily add more devices without overhauling your existing infrastructure. This scalability makes PoE switches ideal for businesses, schools, and even smart homes.
When expanding your network, you don’t need to worry about installing additional power outlets. PoE switches allow you to connect new devices, such as IP cameras or wireless access points, using the same Ethernet cables. This reduces installation time and costs, making it easier to scale your setup.
Tip: Choose a PoE switch with extra ports to future-proof your network. For example, if you currently need eight ports, consider a 16-port switch to accommodate future growth.
PoE switches also support advanced features like power management. You can allocate power efficiently across connected devices, ensuring optimal performance even as your network grows. Managed PoE switches provide even greater control, allowing you to monitor and adjust power settings remotely.
Scalability isn’t just about adding devices. It’s also about flexibility. With PoE technology, you can reposition devices or upgrade to newer models without rewiring. This adaptability ensures your network remains efficient and up-to-date.
Managed PoE switches give you full control over your network. These switches allow you to configure, monitor, and manage network traffic. They include advanced features like VLAN support, Quality of Service (QoS), and SNMP monitoring. These features help you optimize performance and ensure efficient power distribution across connected devices.
You’ll find managed PoE switches especially useful in environments with multiple powered devices. For example, they work well in offices, schools, or data centers where you need to organize cables and reduce clutter. Managed switches also support advanced network setups like Daisy-Chain and Ring Topology, which improve resilience in critical applications. If you need to isolate different network domains while sharing a single distribution point, managed switches can handle that too.
Tip: Managed PoE switches are ideal for large or complex networks where control and scalability are essential.
Unmanaged PoE switches are simpler and easier to use. These plug-and-play devices don’t require any configuration. You just connect your devices, and the switch automatically provides power and data. While they lack advanced features, they’re perfect for small networks or basic setups.
You might use an unmanaged PoE switch in a home or small office where you only need to connect a few devices. For example, they’re great for powering IP cameras, VoIP phones, or wireless access points without the need for complex management. Their affordability makes them a practical choice for budget-conscious users.
Here’s a quick comparison to help you decide which type suits your needs:
Feature | Managed Switches | Unmanaged Switches |
|---|---|---|
Control | Allow configuration, monitoring, and management of network traffic. | Plug-and-play, no configuration needed. |
Features | Advanced features like VLAN support, QoS, and SNMP monitoring. | Basic connectivity without advanced features. |
Cost | Generally more expensive due to advanced capabilities. | More affordable, suitable for basic setups. |
Security | Enhanced security features like 802.1X authentication and access control lists. | Limited security features. |
Scalability | Highly scalable, suitable for complex networks. | Limited scalability, best for small networks. |
When choosing between the two, consider your network size, budget, and need for advanced features. A managed power over ethernet network switch offers more control and scalability, while an unmanaged switch provides simplicity and affordability.

A power over ethernet network switch is an essential tool for powering IP cameras in security systems. It simplifies installation by delivering both power and data through a single Ethernet cable. This eliminates the need for additional power outlets, making it easier to deploy cameras in hard-to-reach areas like ceilings or outdoor locations.
Using PoE switches also allows you to centralize power control. You can monitor and manage power usage from a single location, ensuring that all cameras remain operational. Features like power scheduling and backup options enhance reliability, providing continuous power to critical devices. This is vital for maintaining uninterrupted surveillance in large-scale security networks.
Key benefits of PoE switches for IP cameras include:
Centralized power management.
Cost and time savings.
Flexibility for adding or relocating cameras.
Enhanced reliability for critical operations.
VoIP phones rely on consistent power and data connections to function effectively. PoE switches make deploying these phones in offices straightforward. By transmitting power and data through a single Ethernet cable, PoE eliminates the need for multiple power outlets. This reduces installation costs and simplifies the setup process.
The flexibility offered by PoE switches ensures that you can place VoIP phones in optimal locations for sound coverage and connectivity. Whether you’re setting up a small office or a large corporate network, PoE technology supports seamless communication.
Advantages of PoE for VoIP systems:
Easy deployment with fewer cables.
Flexible device placement for better performance.
PoE switches play a significant role in smart home automation. They simplify installations by combining power and data delivery into a single cable. This reduces the complexity of setting up devices like smart lights, security cameras, and IoT sensors.
Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
Simplified Installations | Devices receive both data and power through one Ethernet cable, reducing installation complexity. |
PoE minimizes the need for extra power outlets and cabling, lowering expenses. | |
Enhanced Flexibility | Devices can be placed in optimal locations without being limited by traditional power sources. |
PoE technology also enhances the freedom to position devices wherever they are most effective. For example, you can install smart cameras in outdoor areas or place IoT sensors in remote corners of your home. This flexibility, combined with cost-effectiveness, makes PoE switches an excellent choice for smart home setups.
Wireless access points (WAPs) play a crucial role in providing seamless internet connectivity across homes, offices, and campuses. Power over Ethernet (PoE) switches enhance the performance and deployment of WAPs by delivering both power and data through a single Ethernet cable. This simplifies installation and allows you to place WAPs in optimal locations, even where power outlets are unavailable.
PoE switches support advanced Ethernet technologies like 2.5GBASE-T, 5GBASE-T, and 10GBASE-T. These technologies improve data transmission speeds, enabling real-time data delivery for high-performance applications. For example, in a busy office or campus, faster data speeds ensure smooth video conferencing, uninterrupted streaming, and reliable connectivity for multiple devices.
Did you know? The IEEE 802.3bt-2018 PoE standard (Type 4) can deliver up to 100 watts of power. This supports high-performance WAPs that require more energy to handle increased data loads and larger coverage areas.
Using PoE switches also simplifies your network infrastructure. By combining power and data delivery into one cable, you reduce the need for additional power outlets. This not only lowers installation costs but also gives you the flexibility to position WAPs where they can provide the best signal strength. Whether it’s a ceiling-mounted WAP in a large conference room or an outdoor unit for campus-wide coverage, PoE makes deployment easier.
Key benefits of PoE switches for WAPs:
Enhanced data speeds for real-time applications.
Simplified installation with fewer cables.
Flexible placement for optimal signal coverage.
Cost savings by eliminating extra power outlets.
With PoE technology, you can create a robust and scalable wireless network that meets the demands of modern connectivity.
PoE switches have specific power limits, which can restrict their ability to support high-performance devices. For example, devices like advanced Wi-Fi access points and PTZ security cameras often require more power than the IEEE 802.3af standard can provide. This standard delivers up to 15.4 watts, but many modern devices exceed this limit.
Devices that may face power constraints include:
High-performance Wi-Fi access points needing more than 12.95 watts.
PTZ cameras requiring extra power for motorized features.
Advanced VoIP phones with large displays.
PoE lighting systems with higher energy demands.
Thin clients and PoE-powered computers.
When powering multiple devices through a splitter, the total power demand can quickly surpass the switch's capacity. To avoid these issues, you should check the power requirements of your devices and ensure compatibility with the PoE standard of your switch.
Ethernet cables used in PoE setups have a maximum effective range of 100 meters (328 feet). Beyond this distance, both power and data signals weaken, which can lead to performance issues. If you need to connect devices located farther away, you may require additional equipment like PoE extenders or repeaters. These tools can help extend the range but add to the overall cost and complexity of your network.
Tip: Plan your device placement carefully to stay within the 100-meter limit and maintain optimal performance.
Not all devices are PoE-compatible, which can create challenges during installation. If you connect a non-PoE device to a PoE switch, it won’t receive power unless you use a PoE splitter or injector. These additional components increase costs and complicate your setup. To avoid compatibility issues, verify whether your devices support PoE before integrating them into your network.
Note: Many modern devices now support PoE, but older or budget models may lack this feature. Always double-check specifications before purchasing.
Understanding the power needs of your devices is crucial when selecting a power over ethernet network switch. Each device, such as IP cameras, VoIP phones, or wireless access points, has specific power requirements. For instance, a basic VoIP phone may need less than 15 watts, while a high-performance PTZ camera could demand up to 90 watts. You should check the power ratings of your devices and ensure the switch supports the required PoE standard, such as IEEE 802.3af or 802.3bt.
To illustrate, here’s a breakdown of power considerations:
Aspect | Findings |
|---|---|
Energy Consumption | Data transmission is the most energy-intensive part of streaming movies. |
Power Requirement | A typical three-sector small cell can require between 200–1,000 watts. |
Energy Efficiency | More than 50% of energy is consumed by computation power at 5G base stations. |
By accurately assessing these needs, you can avoid overloading the switch and ensure reliable performance for all connected devices.
The number of ports on your PoE switch determines how many devices you can connect. Start by listing all the devices you plan to power, such as cameras, phones, and access points. Add a few extra ports to accommodate future growth. For example, if you currently need eight ports, consider a 12- or 16-port switch to allow for expansion.
Tip: Always choose a switch with more ports than you need today. This ensures your network can grow without requiring a complete overhaul.
If you’re managing a small home network, an 8-port switch might suffice. For larger setups, like offices or schools, a 24- or 48-port switch may be more appropriate. Planning ahead saves time and money in the long run.
Your choice between managed and unmanaged switches depends on your network’s complexity and your need for control. Managed switches offer advanced features like VLANs, Quality of Service (QoS), and remote monitoring. These features make them ideal for large or complex networks where precise control is essential. In contrast, unmanaged switches are simpler and more affordable, making them suitable for small networks or basic setups.
Here’s a quick comparison:
Feature | Managed Switches | Unmanaged Switches |
|---|---|---|
Configuration | Extensive customization options | Plug-and-play simplicity |
Scalability | Ideal for complex, growing networks | Limited scalability |
Cost | Higher upfront investment | Budget-friendly |
Security | Enhanced features like ACLs | Basic security |
Note: If you need flexibility and scalability, go for a managed switch. For straightforward setups, an unmanaged switch will do the job.
By evaluating your network’s size, budget, and future needs, you can confidently choose the right switch for your setup.
When choosing a Power over Ethernet (PoE) switch, you need to balance your budget with your network's future needs. A well-planned investment ensures your network remains efficient and adaptable as your requirements grow.
Start by determining how much you can spend. PoE switches come in a wide price range, depending on their features and capabilities. Unmanaged switches are more affordable and work well for small networks. Managed switches, while more expensive, offer advanced features like remote monitoring and VLAN support. These features justify the higher cost for larger or more complex setups.
Tip: If your budget is tight, prioritize essential features like the number of ports and power capacity. You can always upgrade to a managed switch later as your network expands.
Think about how your network might grow in the future. Adding devices like IP cameras, wireless access points, or VoIP phones may require more ports and higher power capacity. Choosing a switch with extra ports now can save you from replacing it later.
Questions to ask yourself:
How many devices do you plan to connect in the next 2–3 years?
Will you need advanced features like power scheduling or remote management?
Are your devices likely to require higher power levels in the future?
Investing in a slightly larger or more advanced switch today can reduce long-term costs. For example, a 16-port managed switch may cost more upfront but will accommodate future growth without additional expenses.
Note: Always consider both your current needs and potential expansion. A scalable solution ensures your network stays reliable and cost-effective over time.
A power over ethernet network switch combines data and power delivery into a single Ethernet cable, simplifying installations and enabling efficient device connectivity. These switches offer numerous benefits, including cost savings, flexibility in device placement, and scalability for growing networks. They are widely used in applications like powering IP cameras, VoIP phones, and wireless access points. However, limitations such as power delivery constraints and distance restrictions should be considered.
The PoE market reflects its growing importance, with a projected value of $10.52 billion by 2032 and a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 21.06%.
Year | Market Value (USD) | CAGR (%) |
|---|---|---|
2023 | 1.89 billion | N/A |
2032 | 10.52 billion | 21.06 |
When choosing a PoE switch, assess your devices' power needs, the number of required ports, and whether you need advanced features like remote management. For small setups, an unmanaged switch may suffice, while managed switches suit larger, more complex networks. By aligning your choice with your current and future needs, you can build a reliable and efficient network.