
Remote work environments demand robust security measures to protect sensitive data. Access control solutions for remote workers, such as Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), Virtual Private Networks (VPNs), and Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA), play a critical role in safeguarding systems. For instance, nearly two-thirds of users now rely on MFA, with 87% of large enterprises implementing it. These tools reduce the risk of breaches while maintaining convenience. By adopting these solutions, you can ensure secure access to your organization’s resources, even in diverse and unsecured network environments.
Use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for better security. MFA adds extra steps, making it harder for hackers to steal data.
Use Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) to keep connections safe. VPNs hide data, protecting access to work networks, especially on public Wi-Fi.
Follow Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) rules. ZTNA always checks users and devices to stop unauthorized access.
Make logging in easier with Single Sign-On (SSO). SSO lets users log in once, keeping it simple and secure.
Teach employees about security often. Training helps them spot dangers and avoid security problems.
Remote work often involves accessing sensitive data from various locations, such as coffee shops, coworking spaces, or home networks. These environments lack the robust security of corporate networks, exposing your organization to potential threats. For example, insecure Wi-Fi connections can allow attackers to intercept data or gain unauthorized access to systems.
A recent study revealed that 86% of business leaders believe global instability could lead to significant cyber incidents in the near future. This highlights the importance of securing remote access points. Without proper measures, your organization risks data breaches and operational disruptions.
Credential theft has become a growing concern in remote work settings. Cybercriminals exploit vulnerabilities in remote environments to steal login information. The Federal Trade Commission reported a doubling of identity theft cases in recent years. Additionally, ZeroFox observed a staggering 519% increase in scams targeting user credentials.
Phishing attacks are one of the most common methods used to steal credentials. During the pandemic, the rapid shift to remote work created opportunities for attackers to exploit unprepared organizations. You can mitigate these risks by implementing strong authentication methods and educating employees about phishing tactics.
Remote workers often use multiple devices, such as laptops, smartphones, and tablets, to perform their tasks. Each device introduces a potential entry point for attackers. Personal devices, in particular, may lack adequate security measures, increasing the risk of unauthorized access.
Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
Compatibility with Existing Systems | Ensuring seamless integration with current systems can lead to conflicts in security protocols. |
User Behavior Management | Unsafe behaviors, such as unauthorized access attempts, pose significant risks. |
Security Risks | Remote access introduces vulnerabilities that need to be addressed through strong policies and tools. |
To address these challenges, you should enforce strict device management policies and ensure all devices meet security standards before granting access to corporate resources.
Balancing security with user convenience is essential for remote work environments. Overly strict security measures can frustrate employees, while lenient policies may expose your organization to risks. To achieve this balance, you need to adopt strategies that prioritize both protection and ease of use.
One effective approach is implementing user-friendly security tools. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and Single Sign-On (SSO) simplify login processes while maintaining robust protection. Password managers also help employees create and store strong passwords without the hassle of remembering them. These tools reduce friction and encourage compliance with security policies.
Clear organizational policies play a crucial role in maintaining this balance. You should establish guidelines for data handling and personal device usage. Employees need to understand what is expected of them to avoid accidental security breaches. Regular training sessions can reinforce these policies and foster a culture of security awareness.
Technical measures also contribute to a seamless yet secure experience. The table below highlights practices that enhance security without compromising usability:
Category | Measures/Practices |
|---|---|
Technical Measures | Strong Authentication (MFA, SSO, Smart Cards) |
Encrypted VPNs (TLS 1.3, IPsec) | |
Regular Patching and Updates | |
Real-time Threat Detection (IDS/IPS, SIEM) | |
Endpoint Security (AV, FW, EDR) | |
Best Practices | Least Privilege Access |
Network Segmentation (VLANs, Subnets) | |
Employee Security Awareness Training | |
Incident Response Planning | |
Cloud-based Solutions | Scalability and Ease of Management |
Cloud Security Gateways (CSG) | |
Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) | |
Key Technologies | Zero Trust Architecture |
Software-Defined Wide Area Networking (SD-WAN) | |
Cloud Access Security Brokers |
By combining these measures with regular updates and real-time threat detection, you can create a secure environment that doesn’t hinder productivity. Remember, the goal is to make security an enabler, not a barrier, for your remote workforce.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is one of the most effective access control solutions for remote workers. It requires users to verify their identity using two or more factors, such as a password and a one-time code sent to their phone. This extra layer of security makes it harder for attackers to gain unauthorized access, even if they steal a password.
MFA significantly reduces the risk of credential theft. For example, phishing attacks often target passwords, but MFA ensures that a stolen password alone is not enough to breach your systems. By implementing MFA, you can protect sensitive data and maintain trust in your remote work environment.
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) create a secure connection between remote workers and corporate networks. They encrypt data, making it unreadable to anyone trying to intercept it. This ensures that sensitive information remains protected, even when employees use public Wi-Fi.
However, VPNs are not without challenges. They can slow down network performance, which may impact productivity. Weak authentication mechanisms in VPNs can also create vulnerabilities. To address these issues, you should scale firewalls and use virtual firewalls to enhance VPN capacity. This ensures that remote workers can access necessary applications without performance problems. Proper tooling, such as instant messaging and conferencing tools, also helps maintain productivity.
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) operates on the principle of "never trust, always verify." It continuously verifies the identity of users and devices before granting access to resources. This approach minimizes the risk of unauthorized access and protects sensitive data.
ZTNA is gaining popularity among organizations. A recent study revealed that 84% of organizations are pursuing Zero Trust for cloud security. Additionally, 69% of respondents rated improved data security as very important, while 67% emphasized the importance of reducing unauthorized access risks. These statistics highlight the growing importance of ZTNA in securing remote work environments.
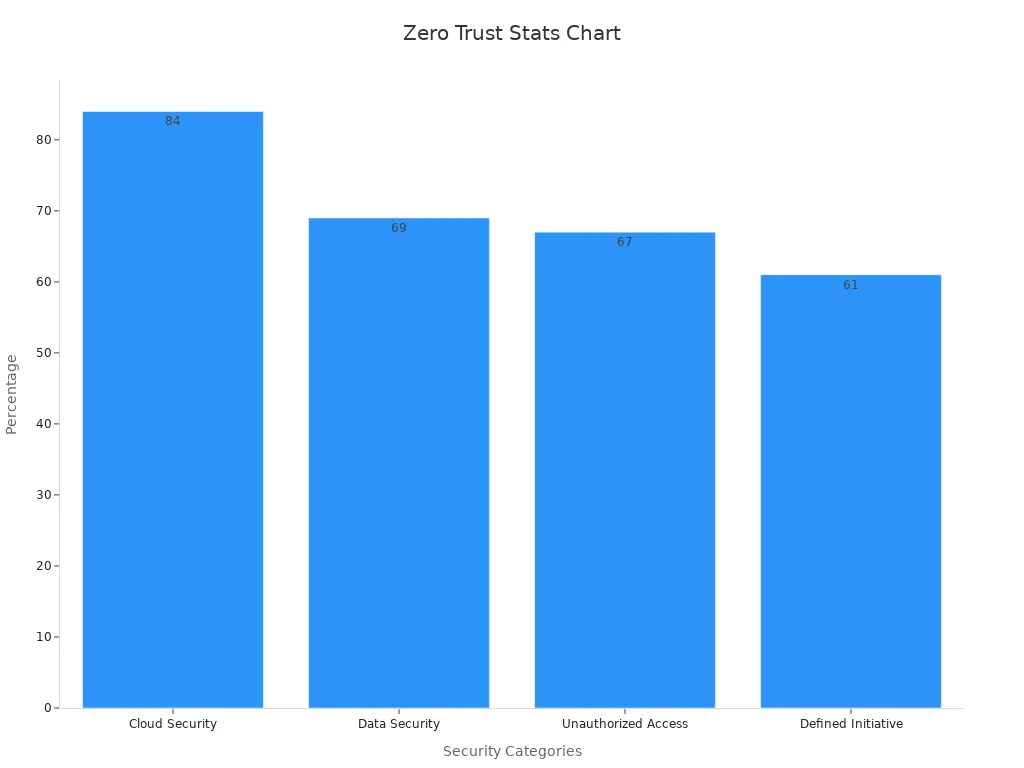
By adopting ZTNA, you can ensure that only authorized users and devices access your corporate resources. This makes it one of the most reliable access control solutions for remote workers.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) is a powerful tool for managing access to your organization's resources. It assigns permissions based on user roles, ensuring employees only access the data and systems they need for their jobs. This approach enhances security by limiting exposure to sensitive information.
RBAC also reduces administrative work. You no longer need to manage individual permissions or frequently update passwords. Instead, you can streamline user management by aligning roles with your organizational structure. This not only saves time but also improves operational efficiency. Employees can focus on their tasks without worrying about unnecessary access restrictions.
Here are some key benefits of RBAC:
Reduces administrative tasks, such as managing passwords.
Maximizes efficiency by aligning roles with job responsibilities.
By implementing RBAC, you can create a secure and efficient remote work environment. It is one of the most effective access control solutions for remote workers.
Endpoint security tools protect the devices your employees use to access corporate resources. These tools include antivirus software, firewalls, and endpoint detection and response (EDR) systems. They monitor and secure devices against malware, phishing attacks, and other threats.
Remote work often involves using personal devices, which may lack proper security measures. Endpoint security tools ensure these devices meet your organization's security standards. They also provide real-time threat detection, allowing you to respond quickly to potential risks.
For example, EDR systems can identify unusual activity on a device, such as unauthorized access attempts. This helps you prevent breaches before they occur. By deploying endpoint security tools, you can safeguard your organization's data and maintain a secure remote work environment.
Single Sign-On (SSO) simplifies the login process for remote workers. With SSO, employees can access multiple applications using a single set of credentials. This reduces the complexity of managing multiple passwords and improves the user experience.
SSO also enhances security. It reduces password-related incidents, such as forgotten passwords or phishing attacks. By integrating SSO with your applications, you can mitigate cybersecurity risks while ensuring seamless access for your employees.
Metrics highlight the impact of SSO:
Reduces login steps from 7-8 to a single click, improving user experience.
Increases productivity by eliminating downtime caused by forgotten passwords.
Operates in the background, ensuring easy adoption by users.
By adopting SSO, you can enhance both security and convenience for your remote workforce. It is a vital component of modern access control solutions for remote workers.
A security audit is the first step in implementing effective access control solutions. It helps you identify vulnerabilities and assess the current state of your security measures. By conducting a thorough audit, you can uncover gaps in your system and prioritize areas that need improvement.
Security audits rely on different types of evidence to ensure accuracy. Documentary evidence, such as policies and procedures, provides a foundation for evaluating existing controls. Observational evidence allows you to assess how well these controls work in real-time. Analytical evidence, like data analysis, helps you detect patterns or anomalies that might indicate security risks.
Type of Evidence | Description |
|---|---|
Documentary Evidence | Involves policies, procedures, and documentation related to security controls, providing a basis for their existence. |
Observational Evidence | Involves direct assessment of security practices, allowing auditors to observe the effectiveness of controls in real-time. |
Analytical Evidence | Involves data analysis to identify patterns or anomalies, helping to uncover potential security issues. |
By using these methods, you can create a detailed roadmap for strengthening your access control systems.
Training your employees is essential for maintaining a secure remote work environment. Regular training sessions teach them how to recognize and respond to cyber threats. This knowledge empowers them to avoid common pitfalls, such as phishing scams or weak passwords.
Continuous education fosters a culture of security within your organization. Research shows that companies with compliant employees experience a breach rate of only 3%, compared to 31% for non-compliant ones. Investing in training not only reduces risks but also boosts employee confidence in handling security challenges.
Compliance Status | Breach Rate |
|---|---|
Non-Compliant | 31% |
Compliant | 3% |
Make training interactive and easy to understand. Use real-world examples to demonstrate the importance of security best practices. This approach ensures employees stay engaged and retain the information.
Integrating access control solutions with your current systems ensures seamless functionality. Start by evaluating your existing infrastructure to identify compatibility issues. Choose solutions that align with your organization’s needs and can scale as you grow.
For example, industries like healthcare and financial services have successfully integrated access controls to meet compliance requirements. In healthcare, robust access controls and encryption improved data security and reduced breaches. Financial services achieved a stronger security posture by deploying secure payment systems and conducting vulnerability assessments.
Industry | Challenge | Solution | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
Healthcare | Ensuring compliance with HIPAA regulations | Implementing robust access controls, encryption, and regular security audits | |
Financial Services | Protecting sensitive payment card information | Deploying encryption, implementing secure payment processing systems, and conducting regular vulnerability assessments | Enhanced security posture and compliance with PCI-DSS requirements |
By integrating access control solutions effectively, you can enhance security without disrupting daily operations.
Keeping your security measures updated and monitored is essential for protecting remote work environments. Cyber threats evolve constantly, and outdated systems become easy targets for attackers. Regular updates and proactive monitoring help you stay ahead of potential risks.
You should prioritize software updates and patch management. These updates fix vulnerabilities that attackers often exploit. Automating updates and scheduling regular patches ensure your systems remain secure without manual intervention. Frequent backups also protect your data from unexpected breaches or system failures.
Monitoring critical systems is equally important. Conducting audits every quarter allows you to identify risks early. Ongoing monitoring ensures that any suspicious activity gets flagged immediately. For example, reviewing and modifying security settings on personal devices can prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
Here are some key practices to follow:
Stay current with software updates to maintain security.
Use centralized identity and access management systems for consistent protection.
Automate updates and schedule regular patches to minimize vulnerabilities.
Perform frequent backups to safeguard your data.
Proactive monitoring also helps you maintain compliance with industry standards. Many regulations require organizations to demonstrate that they actively manage and secure their systems. By implementing these measures, you not only protect your organization but also build trust with your clients and employees.
Regular updates and monitoring create a strong defense against cyber threats. They ensure your remote work environment remains secure and resilient. By adopting these practices, you can reduce risks and maintain a productive workforce.
Simplifying authentication processes can improve security while enhancing the user experience. Complex login procedures often frustrate users, leading to poor compliance or risky shortcuts. By streamlining authentication, you can address these challenges effectively.
Simplified processes reduce the need for multiple complex passwords.
Passwordless methods, such as biometrics or tokens, eliminate vulnerabilities tied to traditional credentials.
Employees, contractors, and partners benefit from faster, more personalized access.
Simpler authentication also reduces the risk of phishing attacks. Passwordless systems, for instance, make it harder for attackers to exploit stolen credentials. Additionally, eliminating frequent password resets improves user satisfaction and productivity.
Metric Description | Implication on Security |
|---|---|
Faster processes reduce frustration and abandonment. | |
Number of attempted account takeover attacks | Fewer attempts indicate stronger security measures. |
Benefits of passwordless authentication | Enhances security and reduces costs for password management. |
By adopting streamlined authentication methods, you can create a secure and user-friendly environment for remote workers.
Single Sign-On (SSO) solutions simplify access to multiple applications with a single set of credentials. This approach enhances both security and convenience for remote workers.
Small businesses use SSO to improve productivity by streamlining cloud application access.
Healthcare organizations comply with HIPAA regulations by securing patient data through SSO.
Financial institutions rely on SSO to protect sensitive financial information.
Studies show that 70% of organizations report improved user experience after adopting SSO. Additionally, 61% experience fewer IT support tickets, reducing operational costs. SSO also enforces consistent authentication policies, strengthening overall security.
By implementing SSO, you can reduce password-related issues and provide seamless access for your team.
Clear guidelines ensure remote workers understand their responsibilities and follow best practices. Effective communication is key to maintaining security and productivity.
Use preferred channels for regular check-ins and updates.
Set clear goals and track performance with reliable tools.
Provide IT support for company hardware and software.
Emphasize secure access methods, such as VPNs, for handling sensitive data.
Guidelines should also address health and safety. Ergonomic setups, regular breaks, and mental health resources help employees stay productive and engaged. By offering clear instructions, you can foster a secure and supportive remote work environment.
Automation plays a vital role in reducing the friction that often comes with security measures for remote workers. By automating repetitive tasks and security processes, you can create a seamless experience while maintaining strong protection for your organization.
One of the biggest challenges remote workers face is dealing with cumbersome security tools. Many employees resort to using personal devices because they find corporate security measures too complex or time-consuming. In fact, 50% of office workers admit to using personal devices for work. This highlights the need for simpler, automated solutions that don’t disrupt workflows.
Automation tools, such as Device Experience (DEX) platforms, can proactively address security issues without requiring user intervention. For example, these tools can automatically fix compliance problems, ensuring devices meet security standards without interrupting your employees. This approach not only enhances security but also allows your team to focus on their tasks without distractions.
Minimizing user interaction with security tools also reduces risks. Automated updates and interventions ensure that systems stay secure without relying on employees to take action. This makes security less intrusive and more effective. For instance, automating software updates and patch management eliminates vulnerabilities that attackers could exploit.
Evidence Description | Key Insight |
|---|---|
Employees use personal devices for work due to cumbersome security tools. | 50% of office workers resort to personal devices, indicating a need for easier security solutions. |
Automation can proactively address security issues without user intervention. | DEX tools can fix compliance issues automatically, enhancing security without disrupting workflows. |
Minimizing user interaction with security tools reduces risks. | The ideal security approach is to automate updates and interventions, making security seamless and less intrusive. |
By leveraging automation, you can simplify security processes, reduce risks, and improve the overall experience for your remote workforce. This ensures that security becomes an enabler of productivity rather than a barrier.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming access control systems by making them smarter and more adaptive. AI-powered solutions analyze user behavior and detect anomalies in real time. This allows you to identify potential threats before they escalate. For example, automated threat detection is expected to become a standard feature in modern access control systems. Businesses are increasingly adopting these tools to enhance security for remote workers.
AI also improves decision-making by processing vast amounts of data quickly. It can recognize patterns that humans might miss, ensuring your systems remain secure. Features like multi-device compatibility and seamless connectivity are becoming essential as remote work continues to grow. By leveraging AI, you can stay ahead of evolving cyber threats and protect your organization’s resources.
Biometric authentication is advancing rapidly, offering faster and more accurate ways to verify identities. Modern fingerprint scanners now work even with dirty or wet fingers, increasing reliability. Enhanced sensors and cameras capture biometric data more quickly, improving the user experience. These advancements make biometrics a practical choice for remote work environments.
AI and machine learning further enhance biometric systems by recognizing subtle patterns in biometric data. This adaptability ensures higher accuracy and security. Integration with traditional methods, such as passwords, boosts user trust and acceptance. As these technologies evolve, you can expect biometric authentication to play a larger role in securing remote access.
Metric | Description |
|---|---|
Accuracy | Modern fingerprint scanners function even with dirty or wet fingers. |
Speed | Enhanced sensors allow faster capture of biometric data. |
User Acceptance | Integration with traditional methods increases trust. |
AI and Machine Learning | Improves adaptability and accuracy by recognizing subtle biometric patterns. |
Passwordless authentication is gaining traction as organizations seek more secure and user-friendly solutions. This method eliminates the need for traditional passwords, reducing the risk of breaches caused by weak or stolen credentials. Innovations like biometrics, FIDO2, and passkeys enhance reliability and ease of use.
Regulatory frameworks, such as HIPAA and GDPR, encourage the adoption of robust access controls. Passwordless methods align with these requirements, making them an attractive option for businesses. Additionally, the market for passwordless authentication is growing rapidly, with forecasts predicting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of up to 28.7%. By adopting passwordless authentication, you can improve security, comply with regulations, and reduce IT costs associated with password management.
NIST 800-63B strongly recommends phishing-resistant methods.
Regulations like HIPAA and PCI mandate robust access controls.
Passwordless systems enhance user experience and eliminate password fatigue.
Zero Trust principles have become a cornerstone of modern access control systems. These principles ensure that no user or device is trusted by default, even within your network. Enhanced integration of these principles provides stronger security while maintaining flexibility for remote workers.
One key improvement is risk-based conditional access. This method evaluates the risk level of each access attempt in real time. For example, if a user logs in from an unfamiliar location, the system may require additional verification. This dynamic approach ensures that only compliant users and devices gain access, reducing potential threats without disrupting workflows.
Another advancement is identity-based segmentation. Traditional access controls relied on static network boundaries, which are less effective in remote work environments. Identity-based segmentation ties access permissions directly to the identity of users or devices. This makes it easier for you to manage access across diverse locations and devices.
The principle of least privilege is also gaining traction. This principle ensures that users only have the permissions they need to perform their tasks. By limiting access, you reduce the risk of exploitation from over-privileged accounts. For example, a marketing employee would not have access to sensitive financial data, minimizing potential vulnerabilities.
Modern systems also emphasize automating context collection. These systems gather data from multiple sources, such as device health and user behavior, to make informed security decisions. Automation allows you to respond to threats in real time, enhancing protection without manual intervention.
Principle | Description |
|---|---|
Risk-based conditional access | Access is granted based on a dynamic evaluation of risk, ensuring only compliant users and devices can proceed, thus enhancing security without disrupting user experience. |
Identity-based segmentation | This approach ties access control directly to user or device identity rather than static network boundaries, making it more flexible and effective. |
Principle of least privilege | Ensures accounts have the minimum permissions necessary, reducing the risk of exploitation from over-privileged accounts. |
Automate Context Collection | Emphasizes the need for comprehensive data collection from various sources to make informed security decisions and respond to threats in real time. |
By adopting these enhanced Zero Trust principles, you can create a secure and adaptable environment for your remote workforce. These advancements ensure that your systems remain resilient against evolving cyber threats.
Access control solutions for remote workers, such as MFA, VPNs, and ZTNA, are essential for protecting sensitive data and ensuring secure access. These tools help organizations adapt to the challenges of remote work while maintaining productivity. For example, 44% of respondents believe access control has become more critical since the pandemic. Additionally, 53% of IT leaders prioritize improving remote access systems, and 70% of organizations report fewer than five serious security incidents annually.
Balancing robust security with user convenience is key. Simplified authentication processes and tools like SSO enhance the user experience while maintaining strong protection. Staying ahead of trends, such as AI-powered systems and passwordless authentication, ensures your organization remains secure and adaptable. Investing in the right solutions creates a seamless and secure remote work environment.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is one of the most secure options. It requires multiple verification steps, such as a password and a code sent to your phone. This makes it harder for attackers to gain access, even if they steal your password.
ZTNA continuously verifies users and devices before granting access. It assumes no one is trustworthy by default. This approach minimizes risks by ensuring only authorized users can access sensitive resources, even in remote work environments.
Yes, SSO simplifies login by allowing you to access multiple applications with one set of credentials. This reduces the need to remember multiple passwords, lowering the chances of password-related incidents like forgetting or reusing weak passwords.
Endpoint security protects the devices you use to access company resources. Tools like antivirus software and firewalls prevent malware and phishing attacks. They ensure your devices meet security standards, safeguarding sensitive data from potential threats.
You can simplify authentication processes by using tools like SSO or passwordless methods. These reduce friction while maintaining strong protection. Clear guidelines and automation also help create a secure yet user-friendly remote work environment.