
When building a reliable gigabit network cable setup, choosing between Cat5e, Cat6, and Cat6a cables can feel overwhelming. Each type offers unique benefits based on speed, bandwidth, and performance. For example:
Cat6 cables handle up to 10 Gbps over 55 meters and operate at 250 MHz, which is more than double the frequency of Cat5e.
Cat6a cables go even further, supporting speeds of 10 Gbps with a frequency of 500 MHz.
Cat5e may work for basic needs, but upgrading to Cat6 or Cat6a ensures better performance and future-proofing for your network.
Cat5e cables are cheap and work well for simple home networks. They can handle speeds up to 1 Gbps.
Cat6 cables are faster, supporting up to 10 Gbps for short distances. They are great for growing businesses.
Cat6a cables are the fastest, handling 10 Gbps over 100 meters. They are perfect for busy places like data centers.
To prepare for the future, pick Cat6 or Cat6a cables. These can handle more data and advanced uses.
Installing cables can be tricky. Cat5e is the easiest, but Cat6a is harder because it is thicker.
Cat5e cables are an enhanced version of the older Cat5 standard. They support speeds of up to 1 Gbps and operate at a frequency of 100 MHz. This makes them suitable for basic gigabit network cable setups. However, their performance can vary based on factors like cable quality, installation practices, and environmental conditions. For example, electromagnetic interference can reduce signal integrity, impacting data transmission efficiency.
Cat5e cables are a cost-effective choice for home networks or small offices where high-speed data transfer is not a priority. They maintain compatibility with most existing network hardware, making them easy to integrate into older systems. Despite their affordability, they lack the advanced features of newer cables, such as reduced crosstalk and higher bandwidth.
Cat6 cables offer a significant upgrade over Cat5e. They support speeds ranging from 1 to 10 Gbps and operate at a frequency of 250 MHz. This higher frequency reduces crosstalk and interference, ensuring more reliable performance in high-speed networks. Engineers test Cat6 cables using Level III testers, which measure signal strength and bandwidth up to 250 MHz. These tests confirm their ability to handle demanding applications like video streaming and online gaming.
Cat6 cables are ideal for gigabit network cable setups in growing businesses or homes with multiple connected devices. They provide a balance between cost and performance, making them a popular choice for modern networks.
Cat6a cables take performance to the next level. They support speeds of 10 Gbps over the full 100-meter length and operate at a frequency of 500 MHz. This makes them twice as capable as Cat6 in terms of bandwidth. Additionally, Cat6a cables minimize crosstalk even further, ensuring stable and efficient data transmission.
These cables are perfect for high-performance environments like data centers or smart homes with advanced automation systems. Their ability to handle large amounts of data makes them a future-proof option for gigabit network cable installations.
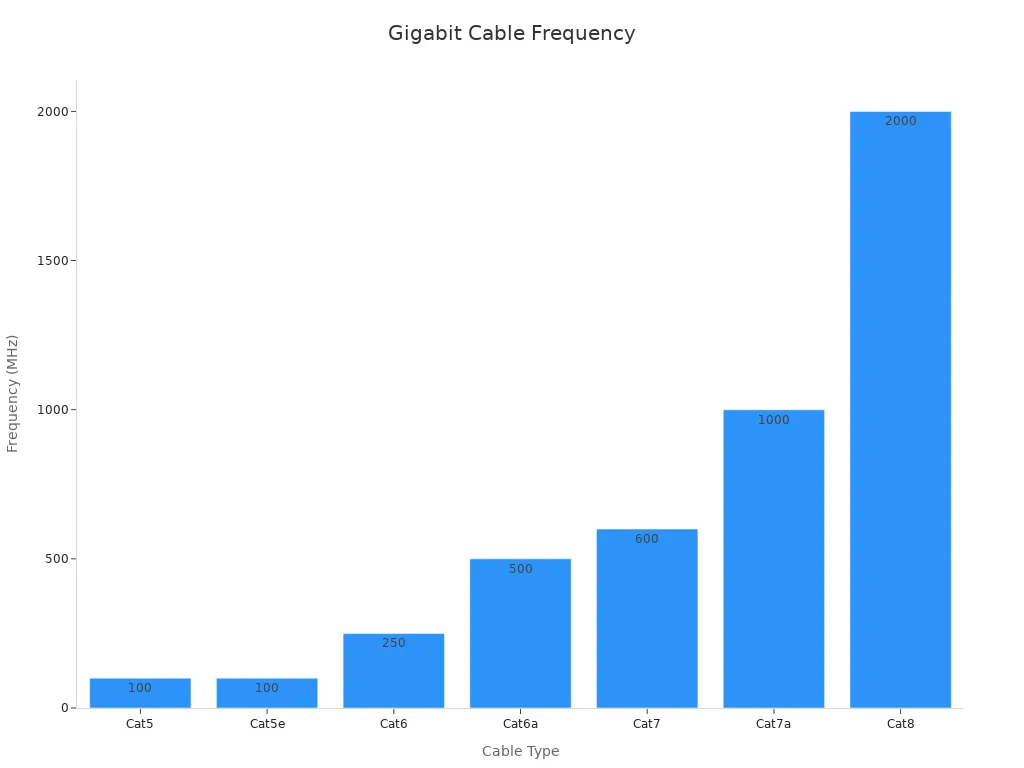

When comparing the maximum speeds of Cat5e, Cat6, and Cat6a cables, you’ll notice significant differences that impact their suitability for various applications. Cat5e cables support speeds of up to 1 Gbps, which is sufficient for basic residential or small office networks. However, if you require faster data transfer, Cat6 and Cat6a cables are better options. Cat6 cables can handle speeds of up to 10 Gbps, but only over shorter distances of up to 55 meters. On the other hand, Cat6a cables maintain 10 Gbps speeds over the full 100-meter length, making them ideal for high-performance environments.
Here’s a quick comparison of maximum speeds and other key metrics:
Ethernet Cable | Max Data Transfer Speed | Max Bandwidth | Optimal Cable Length for Max Speed | Common Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Cat5e | 1 Gbps | 100 MHz | Up to 100 meters | Residential networking, basic office use |
Cat6 | 10 Gbps | 250 MHz | Up to 55 meters for 10 Gbps, 100 meters for lower speeds | General office networking, some data center applications |
Cat6a | 10 Gbps | 500 MHz | Up to 100 meters | Advanced office networks, data centers, industrial applications |
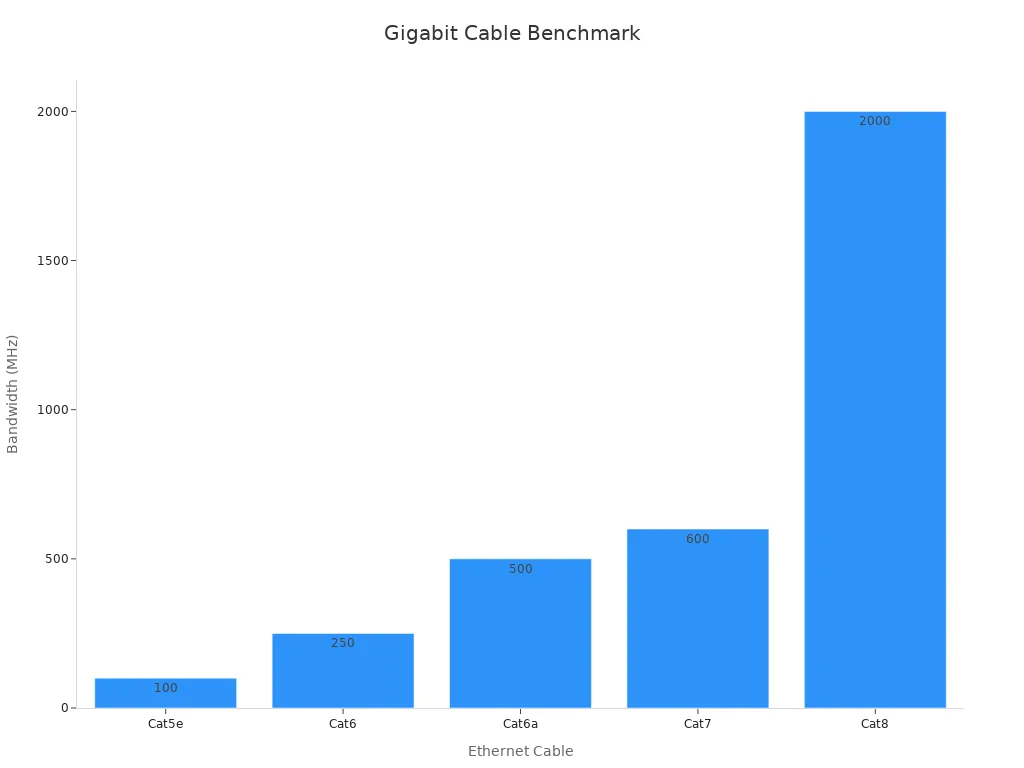
Bandwidth determines how much data your cable can transmit at once. Cat5e cables operate at a bandwidth of 100 MHz, which is sufficient for basic gigabit network cable setups. However, as your network demands grow, you may find this bandwidth limiting. Cat6 cables offer a significant improvement with a bandwidth of 250 MHz, allowing for smoother performance in environments with multiple connected devices. Cat6a cables double this capability, operating at 500 MHz. This higher bandwidth ensures minimal interference and supports advanced applications like video conferencing and large file transfers.
To visualize the differences in bandwidth capabilities, refer to the chart below:
The distance a cable can maintain optimal performance is another critical factor to consider. Cat5e cables can transmit data effectively over distances of up to 100 meters. Cat6 cables, while capable of higher speeds, experience signal degradation beyond 55 meters when operating at 10 Gbps. For lower speeds, they can still perform well up to 100 meters. Cat6a cables excel in this area, maintaining 10 Gbps speeds over the full 100-meter length.
Several factors influence these distance limitations:
The signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) plays a significant role in maintaining performance. Cat6 cables handle noise better than Cat5e due to their improved design.
High-temperature environments can reduce the maximum allowable cable length.
Crosstalk and signal integrity are tested rigorously to ensure cables meet performance standards.
If you’re planning a gigabit network cable installation, consider the layout of your space and the distance between devices. For longer runs, Cat6a cables provide the most reliable performance.
When comparing Cat5e, Cat6, and Cat6a cables, you’ll notice significant price differences. Cat5e cables are the most affordable option, making them ideal for budget-conscious users. However, their lower cost comes with limited performance. Cat6 cables strike a balance between cost and performance, offering speeds up to 10 Gbps over shorter distances. Cat6a cables, while more expensive, provide superior performance with 10 Gbps speeds over 100 meters.
Here’s a quick comparison of costs and use cases:
Cable Type | Cost | Performance | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
Cat5e | Lowest | Up to 1 Gbps | Home and small office networks |
Cat6 | Moderate | Up to 10 Gbps at 55m | Growing businesses, advanced home setups |
Cat6a | Higher | 10 Gbps at 100m | Data centers, high-demand environments |
Recent market trends show that Cat6 cables lead in popularity due to their cost-performance balance. However, rising copper prices have increased the overall cost of all cable types, making cost efficiency a key consideration for buyers.
The complexity of installing network cables depends on the type you choose. Cat5e cables are the easiest to install due to their flexibility and compatibility with older hardware. Cat6 cables require more precision during installation to minimize crosstalk and interference. Cat6a cables, with their thicker shielding, demand even greater care and expertise.
For example, in a case study involving a city-wide CCTV installation, engineers used Cat6 cables to transmit high-definition video data over long distances. They faced challenges like ensuring signal integrity and managing cable durability in outdoor conditions. This highlights the importance of proper planning and skilled labor for complex installations.
When upgrading your gigabit network cable, compatibility with existing hardware is crucial. Cat5e cables work seamlessly with older devices, making them a practical choice for basic setups. Cat6 and Cat6a cables, while backward compatible, may require updated network equipment to achieve their full potential.
If your network includes older routers or switches, you might need to upgrade these components to fully utilize the capabilities of Cat6 or Cat6a cables. This additional expense can impact your overall budget, so it’s essential to evaluate your current infrastructure before making a decision.
When setting up a home network, you want a solution that meets your current needs while preparing for future demands. Cat5e cables work well for basic activities like streaming, online gaming, and web browsing. They are affordable and easy to install, making them a popular choice for households with standard internet speeds.
If your home includes multiple smart devices or you plan to upgrade to high-speed internet, Cat6 cables offer better performance. They provide faster speeds and greater stability, ensuring smooth connectivity even with multiple users. For example, surveys show that Cat6 cables are ideal for homes with smart devices and high-speed internet plans.
For those looking to future-proof their home network, Cat6a cables are the best option. They support higher bandwidth and faster speeds, making them suitable for advanced applications like 4K streaming and smart home automation. As data demands increase, these cables ensure your network remains reliable and efficient.
Small businesses often face unique challenges when building their networks. You need a solution that balances cost, performance, and scalability. Cat5e cables can handle basic office tasks like email, file sharing, and video conferencing. However, as your business grows, these cables may struggle to keep up with higher data demands.
Cat6 cables provide a significant upgrade for small businesses. They support faster speeds and higher bandwidth, making them suitable for environments with multiple employees and connected devices. For example, a small office with 10-20 employees can benefit from the improved performance of Cat6 cables, especially when using cloud-based applications or hosting virtual meetings.
For businesses planning to expand, Cat6a cables offer the best long-term value. They support 10 Gbps speeds over 100 meters, ensuring reliable performance even in larger office spaces. Reports highlight the importance of future-proof cable management in small business networks, emphasizing the need for adaptable solutions that can scale with your operations.
Key Insights | Description |
|---|---|
Future-proof Cable Management | Seamless integration of new hardware and cables during business expansion. |
Importance of Cable Organization | Central to efficient scalability efforts as office layouts evolve. |
Adaptable Solutions | Essential for smooth transitions without disrupting ongoing operations. |
Data centers and high-demand environments require the most advanced cabling solutions. You need cables that can handle massive data traffic while maintaining efficiency and reliability. Cat6a cables are the minimum standard for these applications, offering 10 Gbps speeds and superior resistance to interference.
Projections show that fiber optic cables are gaining popularity in data centers due to their ability to support high-speed internet and advanced technologies like 5G and IoT. However, Cat6a cables remain a cost-effective alternative for many organizations. They provide the performance needed for cloud computing, big data analytics, and other high-demand applications.
Industry reports highlight the benefits of advanced Ethernet cables in data centers:
Vendors are introducing innovative cabling solutions to meet rising demands.
High-performance cables enhance operations and minimize downtime.
Sustainable practices are driving the development of eco-friendly cabling materials.
For future-proofing, consider the scalability and adaptability of your cabling system. Open-source fiber networks, for example, allow users to switch service providers easily and support a large number of connections in small areas. These features ensure your network can evolve with technological advancements.
Key Insights | Description |
|---|---|
Open-source Fiber Network | Allows every potential user to have dedicated fiber connections. |
Flexibility in Service Providers | Changing service providers is as simple as changing patchcords. |
Scalability | Supports a large number of connections for a small residential area. |

Electromagnetic interference (EMI) can disrupt data transmission, especially in environments with high-frequency noise. Choosing the right cable type helps you minimize these disruptions. Cat5e cables offer basic EMI resistance but may struggle in noisy environments. Cat6 cables, particularly shielded ones, provide better protection against interference. Shielding techniques, such as foil or braided layers, block external noise and maintain signal integrity.
Here’s a comparison of EMI resistance across cable types:
Cable Type | Data Rate (Gbps) | Bandwidth (MHz) | Signal Integrity |
|---|---|---|---|
Cat5e | Up to 1 | 100 | Lower resistance to EMI |
Cat6 (Unshielded) | 250 | Moderate resistance to EMI | |
Cat6 (Shielded) | Up to 10 (55m) | Increased capacity | Superior resistance to EMI |
For environments with heavy interference, shielded Cat6 or Cat6a cables ensure stable performance.
Durability is essential for cables exposed to harsh conditions. Modern cables use advanced materials to withstand environmental challenges. For example:
UV Radiation: UV-resistant jackets prevent damage from sunlight.
Temperature Extremes: Flexible materials ensure functionality in extreme heat or cold.
Moisture Resistance: Waterproof designs protect internal components from corrosion.
Physical Damage: High-density polyethylene jackets resist abrasion and impact.
Pest Interference: Rodent-resistant materials deter animal damage.
These features make Cat6a cables particularly robust, ideal for outdoor installations or industrial settings.
The choice between shielded and unshielded cables depends on your environment. Shielded cables manage EMI effectively but require grounding, which complicates installation. Unshielded cables are more flexible and cost-effective, performing well in low-interference areas.
Shielded Cables: Best for high-EMI environments but more expensive and less flexible.
Unshielded Cables: Easier to install and suitable for most residential or office setups.
Understanding your network’s electrical and environmental conditions helps you decide which option fits your needs.
Choosing the right gigabit network cable depends on your needs and priorities. Cat5e cables work well for basic setups, offering affordability but limited future-proofing. Cat6 cables balance cost and performance, making them suitable for growing networks. For high-demand environments, Cat6a cables deliver superior speed, bandwidth, and durability. Investing in higher-quality cables may seem costly upfront, but it reduces maintenance and ensures long-term reliability. Evaluate performance, cost, and durability to make the best decision for your network.
Cat5e supports speeds up to 1 Gbps, while Cat6 handles up to 10 Gbps over shorter distances. Cat6a maintains 10 Gbps over 100 meters and offers better interference resistance. Choose based on your speed and distance needs.
Yes, Cat6 and Cat6a cables are backward compatible. They work with older devices but may not deliver their maximum performance unless paired with updated hardware.
Shielded cables are not usually required for home networks. They are best for environments with high electromagnetic interference, like industrial areas. Unshielded cables work well in most residential setups.
Choose Cat6 or Cat6a cables for higher speeds and bandwidth. These cables support advanced applications like 4K streaming and smart home automation. They ensure your network can handle future data demands.
Yes, longer runs can reduce performance. Cat5e and Cat6 cables maintain optimal speeds up to 100 meters for lower data rates. For 10 Gbps speeds over long distances, use Cat6a cables.